Young camper diagnosed with life-threatening Powassan virus during northern Ont. trip
A nine-year-old boy contracted an often-deadly disease during a in northern Ontario camping trip in July.
The Canadian Medical Association Journal (CMAJ) detailed the boy's battle with the Powassan virus, which officials believe he contracted from a tick bite.
Thankfully, he recovered despite becoming severely ill. The CMA said it was publishing the story in hopes of raising awareness of the virus to help speed up the diagnosis of patients in the future. Information on where the boy was camping and where he is from was not included in the story.
Powassan is a tick-borne flavivirus first discovered in 1958 in Powassan, Ont., after being isolated from the brain tissue of a child who died from the virus.
"Increased awareness of Powassan virus among clinicians in Canada will likely lead to increased identification of Powassan virus and other arthropod-borne infections, which should always be reported," the CMAJ story said.
The youngster was hospitalized in July after suffering from severe neck stiffness, fever and a headache for about one day.
"Symptoms began one week after he attended a summer camping trip in northern Ontario," the story in the CMA Journal reported.
"On arrival at the hospital, the patient was febrile (feverish) and appeared unwell, though he was hemodynamically stable and the neurologic exam was normal at the time."
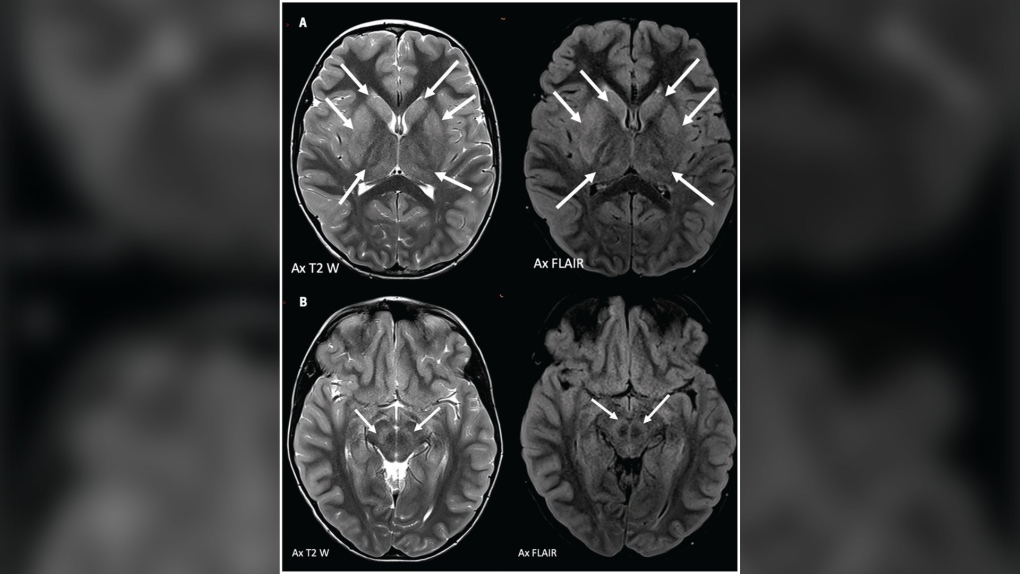 The Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) of the brain of the nine-year-old boy who contracted the Powassan virus during a northern Ontario camping trip in July. (Photo courtesy of the Canadian Medical Association Journal)
The Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) of the brain of the nine-year-old boy who contracted the Powassan virus during a northern Ontario camping trip in July. (Photo courtesy of the Canadian Medical Association Journal)
He had no rashes and doctors suspected that he was suffering from meningitis. That was eventually ruled out through testing, along with several other possible conditions.
"The patient remained persistently febrile with ongoing severe headache," the story said.
"On the third day of hospital admission, the patient was transferred to our tertiary care hospital’s pediatric intensive care unit, because his level of consciousness was deteriorating."
At that point, he couldn't speak or respond to verbal commands and appeared to be in a coma. An MRI showed slowing brain activity, but no evidence of a brain seizure.
Brain swelling
More conditions – including Lyme disease – were ruled out. Samples were sent to Public Health Ontario, but results didn't come back before he recovered enough to leave hospital.
He was given antibiotics to address brain swelling, "with notable improvement in his level of consciousness within 24–48 hours," the story said.
"We discontinued antibiotics after a total of five days once bacterial cultures were found to be negative. The patient was subsequently transferred to the inpatient pediatric ward for 10 days for rehabilitation related to a persistent left-sided weakness."
Two months after he was discharged, "he had full neurologic recovery," the story said.
"After discharge, Public Health Ontario notified us that serum antibodies to Powassan virus were detected."
"Transmission to humans occurs predominantly via the bite of infected ticks … which become infected after feeding on deer, groundhogs, mice, squirrels or other rodents," the CMA story said.
"Research in animal models has suggested that Powassan virus can be transmitted within 15 minutes of tick attachment."
o Download our app to get local alerts on your device
o Get the latest local updates right to your inbox
It's a rare virus, with most cases occurring from April to November.
From 2004 to 2022, the U.S. reported 288 cases of Powassan virus infection. Of those, 25 per cent occurred in children and 92 per cent of those infected had to be hospitalized.
A total of 36 – or 13 per cent – of the patients died.
"Only 21 cases have been reported in Canada since 2017, but a lack of clinical recognition, and hence testing, may result in underestimation of the incidence," the CMAJ story said.
"Most patients experience flu-like symptoms lasting a few days; however, some patients will develop neuroinvasive disease presenting with symptoms characteristic of viral encephalitis, including fever, headache and altered mental status."
About 50 per cent of people who get the virus have long-term effects, "including headaches, altered mental status, and cognitive difficulties."
Read the full CMAJ report here.
CTVNews.ca Top Stories

opinion Tom Mulcair: Prime Minister Justin Trudeau's train wreck of a final act
In his latest column for CTVNews.ca, former NDP leader and political analyst Tom Mulcair puts a spotlight on the 'spectacular failure' of Prime Minister Justin Trudeau's final act on the political stage.
B.C. mayor gets calls from across Canada about 'crazy' plan to recruit doctors
A British Columbia community's "out-of-the-box" plan to ease its family doctor shortage by hiring physicians as city employees is sparking interest from across Canada, says Colwood Mayor Doug Kobayashi.
'There’s no support': Domestic abuse survivor shares difficulties leaving her relationship
An Edmonton woman who tried to flee an abusive relationship ended up back where she started in part due to a lack of shelter space.
opinion King Charles' Christmas: Who's in and who's out this year?
Christmas 2024 is set to be a Christmas like no other for the Royal Family, says royal commentator Afua Hagan. King Charles III has initiated the most important and significant transformation of royal Christmas celebrations in decades.
Baseball Hall of Famer Rickey Henderson dead at 65, reports say
Rickey Henderson, a Baseball Hall of Famer and Major League Baseball’s all-time stolen bases leader, is dead at 65, according to multiple reports.
Arizona third-grader saves choking friend
An Arizona third-grader is being recognized by his local fire department after saving a friend from choking.
Germans mourn the 5 killed and 200 injured in the apparent attack on a Christmas market
Germans on Saturday mourned the victims of an apparent attack in which authorities say a doctor drove into a busy outdoor Christmas market, killing five people, injuring 200 others and shaking the public’s sense of security at what would otherwise be a time of joy.
Blake Lively accuses 'It Ends With Us' director Justin Baldoni of harassment and smear campaign
Blake Lively has accused her 'It Ends With Us' director and co-star Justin Baldoni of sexual harassment on the set of the movie and a subsequent effort to “destroy' her reputation in a legal complaint.
Oysters distributed in B.C., Alberta, Ontario recalled for norovirus contamination
The Canadian Food Inspection Agency has issued a recall due to possible norovirus contamination of certain oysters distributed in British Columbia, Alberta and Ontario.

































